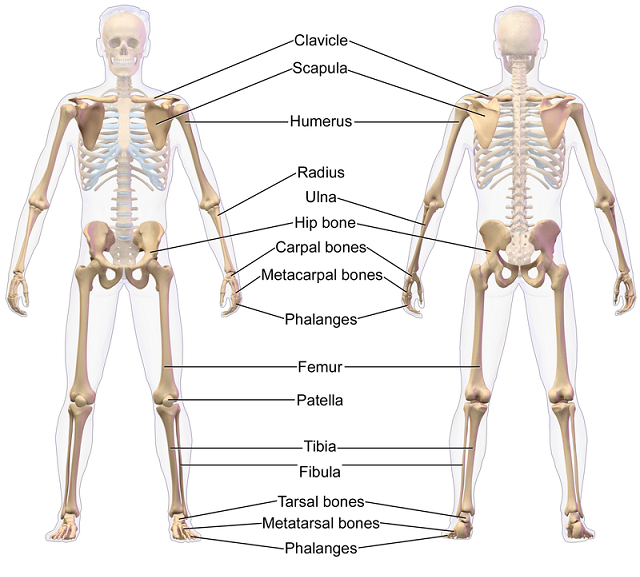
The human skeletal system is comprised of 206 bones. Many of the bones form moving joints. There are also several hundred miles of muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The bones provide the body structure but the ligaments and tendons provide the attachments necessary for the muscles to contract and relax.
The illustration above shows a few of the major bones in the human body. The illustration above is of an Appendicular Skeleton. The appendicular skeleton normally includes the arms, hands, legs, and feet. The Axial Skeleton (not shown) includes the head, chest, and pelvis. It includes everything except the arms, hands, legs, and feet.
The skeletal system obviously has its own medical terms. The chart below lists the root words for some of the medical terms you’re likely to encounter.
| Skeletal System and Joints Root Words | |
| Arthr/o | joint |
| Articul/o | joint |
| Burs/o | bursa |
| Chondr/o | cartilage |
| Disk/o | intervertebral disk |
| Fibros/o | fibrous |
| Kyph/o | humpback |
| Lamin/o | lamina |
| Lord/o | curve or swayback |
| Lumb/o | lumbar region of lower back |
| Meninsc/o | meniscus |
| Myel/o | bone marroe |
| Oste/p | bone |
| Orth/o | straight |
| Scoli/o | curvature or crooked |
| Spondyl/o | vertebra (conditions of the vertebrae structure) |
| Synovi/o | synovium |
| Ten/o, Tend/o, or Tendin/o | tendon |
| Vertebr/o | vertebra (describing the vertebrae structure) |
Get ready! Below is a list of common medical terms you’re likely to encounter for skeletal conditions, diagnoses, treatments, and procedures. We will include a printable version of the list later on this page..
| Common Medical Terms Associated With the Skeletal and Joints System | |
| Acetabulum | Hip joint |
| Ankulosing spondylitis | Chronic arthritis with stiffening of the joints. |
| Ankylosis | Joint stiffness |
| Arthralgia | Joint pain |
| Arthritis | Inflammation of a joint |
| Arthrocentesis | Surgical puncture of a joint to aspirate fluid to be diagnosed. |
| Arthrogram | An x-ray film of a joint |
| Articular cartilage | Cartilage that cushions ends of long bones |
| Articulation | Another name for joint. |
| Bradykinesia | Slow movement |
| Bursa | A sac of fluid at or around a joint |
| Calcium | One of the mineral components of a bone |
| Cancaneus | Heel |
| Cancellous bone | Spongy, porous bone tissue |
| Carpals | Wrist bones |
| Chiropodist | A specialist in diagnosing and treating foot disorders. |
| Chiropractics | A system of therapy that involves maniuplation of the vertebral column. |
| Chiropractor | A specialist in chiropractics |
| Chrondromalacia | Softening of cartilage |
| Computerized Tomorgraphy (CT) | Test to provide accurate definition of bone structure. |
| Compact bone | Hard, dense bone tissue |
| Condyle | Knuckle-like process at the end of a bone, near the joint. |
| Costal | Ribs |
| Diaphysis | Middle region of a long bone |
| Dyskinesia | Difficult movement |
| Dystrophy | Abnormal movement |
| Epiphysis | End of a long bone |
| Fissure | Narrow opening between bones |
| Fluoroscopy | An examination using a fluoroscope |
| Fontanelle | Soft spot. Incomplete closure on infant’s skull sutures |
| Fossa | Cavity or depression in a bone |
| Gouty arthritis | Inflammation of the joints caused by excessive uric acid in the body. |
| Hematopoiesis | Development of blood cells in bone marrow |
| Hematopoietic | Blood cell forming |
| Hyperkinesia | Excessive movement or overactivity |
| Intercostal | Within the cranium |
| Kyphosis | Abnormal hunch of thoracic spine |
| Ligament | Tissue that connects bones to other bones. |
| Magnetic Resonant Imaging (MRI) | Procedure to evaluate soft tissues, ligaments, tendons, muscles, spinal stenosis, and degenerative disk changes. |
| Malleolus | Ankle |
| Mandible | Upper jaw |
| Mastoid process | Round projection on the temporal bone behind the ear. |
| Maxilla | Lower jaw |
| Meniscectomy | Excision of a meniscus for a torn cartilage in the knee. |
| Orthopedics | Field of medicine that focuses on the study and treatment of the skeletal system. |
| Orthopedist | A specialist in orthopedics |
| Orthotics | Manufacture and fitting of orthopedic appliances used to support, align, or correct deformities. |
| Ossification | Process of bone formation |
| Osteoarthritis | Chronic inflammation of the bones and joints due to degenerative changes in the cartilage. |
| Osteoblast | A bone cell that helps form bone tissue. |
| Osteoclasis | Surgical breaking of a bone to correct a deformity. |
| Osteoclast | A bone cell that removes unwanted bone tissue. |
| Osteogenic sarcoma | Malignant tumor of a bone. |
| Osteomyelitis | Inflammation of the bone and marrow due to infection. |
| Osteopath | A specialist in ostopathy |
| Osteopathy | Field of medicine that emphasized the relationship between the body organs and the skeletal system. |
| Osteoplasty | Surgical repair of a bone |
| Osteoporosis | Loss of bone density |
| Osteotomy | Incision into a bone |
| Patella | Knee cap |
| Patellectomy | Excision of the knee cap |
| Periosteum | Strong, fibrous membrane that covers the surface of a bone except at the ends |
| Phlanges | Bones of the fingers or toes |
| Physis | Also called growth plate (of a long bone) |
| Podiatrist | A specialist in foot disorders. |
| Prosthesis | An artificial replacement for a missing body part. |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Chronic disease with inflamed and painful joints. |
| Rickets | Inflammation of the spinal column. |
| Salter-Harris system | Classification system used to identify bone fracture |
| Scoliosis | An abnormal curvature of the spine. |
| Synovial joints | Joints that can move freely. |
| Tendonitis | Inflammation of a tendon |
| Tenodynia | Pain in a tendon |
| Tenorrhapy | Suturing of a tendon |
| Tenotomy | Incision of a tendon |
| Trochanter | Large process behind the neck of the femur |
| Tubercle | Small, rounded process of a bone |
| Tuberosity | Large rounded process of a bone |
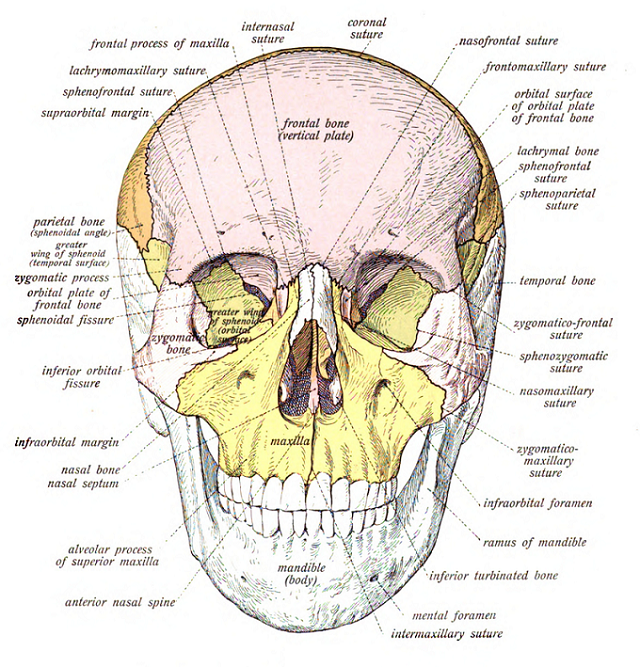
The cranium or skull contains the eight cranial bones. These include the frontal bone, two parietal bones, two temporal bones, the occipital bone, the sphenoid bone, and the ethmoid bone.
The facial bones are all joined together except the mandible or lower jaw bone. Other facial bones include two nasal bones, two maxillae bones, two lacrimal bones, two zygomatic bones, two palatine bones, two inferior nasal concha bones, the vomer bone, and the hyoid bone.
The middle ear bones are often overlooked because they’re so tiny. These bones include the malleus, the incus, and the stapes. Obviously there are two pair of each bone, one for each ear.
The vertebral column or spinal column consists of 26 bones segments called vertebrae. The vertebrae are divided into five divisions known as cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, and coccyx. The chart below further explains the five divisions of the spinal column
| Regions of the Human Spinal Column | |
| Cervical region | Located in the neck region. There are seven cervical vertebrae numbers from C1 to C7. |
| Thoracic or Dorsal region | Located in the chest region. There are 12 thoracic or dorsal vertebrae number from T1 to T12 or D1 to D12. |
| Lumbar region | Located between the ribs and the hip bone. There are five lumbar vertebrae number from L1 to L5. |
| Sacral region | There are five bones numbers S1 to S5 that are fused together to form the sacrum. |
| Coccygeal region | Includes the coccyx which is 4 pieces fused together. |
The thorax starts with the collarbone, which is technically called the clavicle The collarbone connects the sternum or breastbone to each shoulder blade (scapula.) Below the thorax are 12 pairs of ribs. These include 7 pairs of ribs directly attached to the sternum, 3 pairs of ‘false ribs,” and 2 pairs of floating ribs.
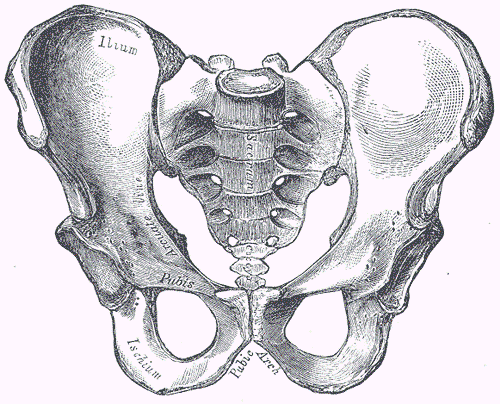
The hip bone is also called the pelvic girdle. This large bone supports the torso and joins with the femur (thigh bone) and sacrum. An adult pelvic bone consists of three pairs of bones fused together – the ilium, the ischium, and the pubis. The diagram below shows the pelvis of an adult male.
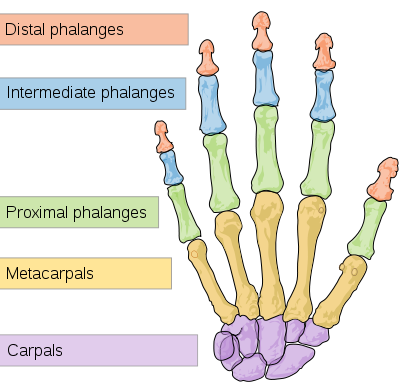
Hands and arms are classified as upper extremities. There are five bones in each arm and 27 bones in each hand. The bones in the arm include the clavicle, the scapula, the humerus, the ulna, and the radius. The bones in the hand include the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The bones in the fingers include the metacarpus, proximal phalanges, intermediate phalanges, and distal phalanges. The diagram below shows the bones in a hand.
Since the hands and arms are referred to as the upper extremities, it doesn’t take much to surmise what legs and feet are called. Legs and feet are classified as lower extremities. There are six bones in the leg and 26 bones in each foot. The bones in the leg include the hip bone (consisting of the fused ilium, ischium and pubis), pelvis, femur, patella (knee cap), tibia, and fibula. The bones in the foot include the calcaneus, talus, navicular, medial cuneiform, lateral cuneiform, metatarsus, sesamoid, and cuboid. The bones in the toes include the proximal phalanges, intermediate phalanges, and distal phalanges.